ResLysEmbed: A ResNet-Based Framework for Succinylated Lysine Residue Prediction Using Sequence and Language Model Embeddings
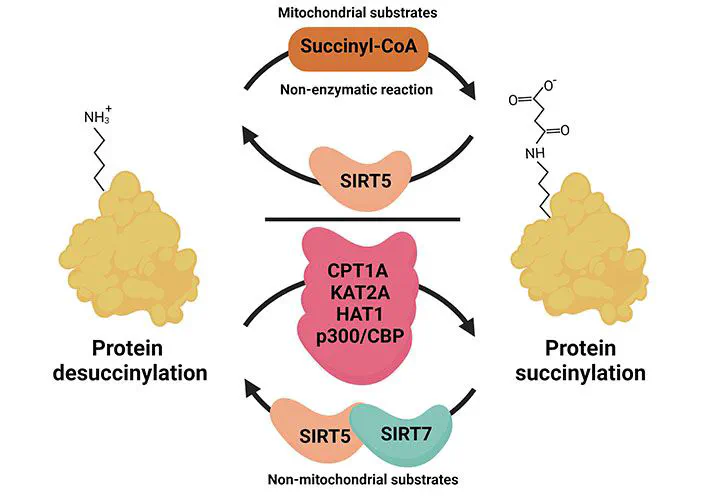 How Succinylation works
How Succinylation worksAbstract
Lysine (K) succinylation is a crucial post-translational modification linked to diverse biological processes and diseases. Current computational methods remain limited in predictive power and interpretability. We present ResLysEmbed, a novel hybrid ResNet-based framework that integrates traditional word embeddings with protein language model embeddings (ProtT5) for succinylation site prediction. ResLysEmbed consistently outperforms existing methods, achieving accuracy, MCC, and F1-scores of 0.81/0.39/0.40 and 0.72/0.44/0.67 on two independent test sets, respectively. Comparative evaluations against other PLMs (PTM-Mamba, ESM-650M, ESM-3B) demonstrate ProtT5 as the most effective embedding choice. Furthermore, SHAP-based interpretability analysis reveals biologically meaningful insights into residue contributions within a 33-mer sequence window, reaffirming the biological relevance of our predictions. ResLysEmbed thus establishes itself as a robust and computationally efficient framework for lysine succinylation prediction.
Type
Publication
Bioinformatics Advances
Click the Cite button above to import this publication into your reference manager.
This work introduces a new hybrid ResNet-based model for succinylation prediction, integrates multiple PLM embeddings, and applies SHAP analysis for biological interpretability.